When you buy through links on our site , we may realise an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Unusual structures on moth eyes that help the insects see at Nox have inspired a new anti - reflection pic for electronic gadget . The new engineering science could help exploiter see their screens even in bright daylight .
The cinema significantlyreduces glareas well as the penury to sidestep into the shade to read what ’s on the concealment .

" For most commercial-grade smartphones , the moth - heart moving picture can improve the legibility of the screen by 10 times under a clear sky . Under direct sunshine , the readability can be improved by five times , " say physicist Shin - Tson Wu , a professor in the College of Optics and Photonics at the University of Central Florida ( UCF ) . [ 7 Things You Do n’t Know About moth , But Should ]
The nature - inspired film is expected to be inexpensive to manufacture , he said , and has the add benefit of being excoriation - resistant and self - cleaning . Users could finally rid their phones of the detritus , fingerprints and grunge that tend to collect on regular sense of touch CRT screen , the researcher describe .
The researchers described their engineering in a survey publish online June 22 in thejournal Optica .
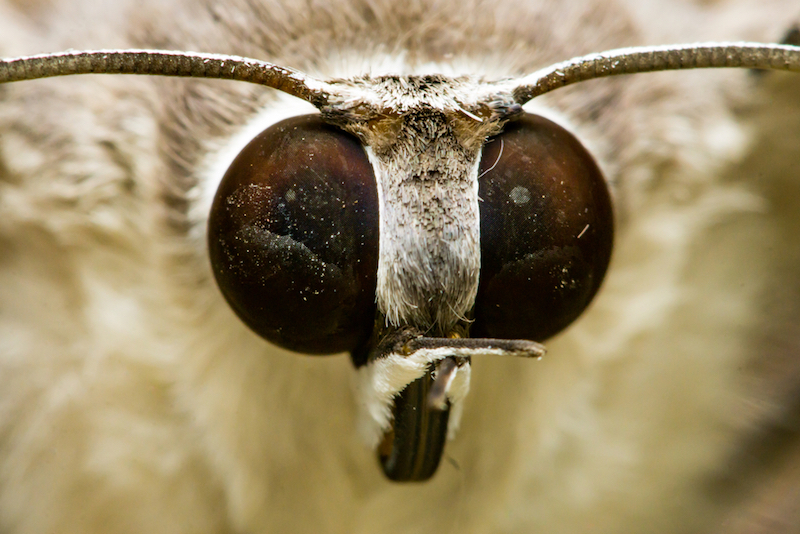

Wu ’s team , admit Guanjan Tan , the study ’s lead author , and Jiun - Haw Lee ’s team from National Taiwan University ( NTU ) , were inspired to modernise the anti - pensive film after get word about the so - holler moth - center effect . This term refer to the unique blueprint of anti - pondering nanostructures on the forbidden surface of a moth ’s corneas .
The nanostructuresallow light to pass into the eyes , but do n’t allow it to shine out . This helps moths see in the dark but also prevents their eyes from reflecting luminance that might give the worm away to predators .
Other scientists inspired by this adaption in moths made solar cadre with nanostructured open to abbreviate the amount of sunshine that reflected away from the panels . This helps hike efficiency . Wu and Tan mean the technique could serve as a low - cost resolution to ameliorate the legibility ofelectronic display .

Many smartphones and laptop have been design to solve the problem of glare using a sensor that detects the quality of light and can heighten the brightness or even dim the screen according to the surround . But increasing the display brightness typically drains a gimmick ’s battery .
With this new coating , no additional might is ask .
" The moth - eye - similar nanostructure film can be manufacture and sold as anaccessory for our devices , just like screen - protection movie , " Wu pronounce . Or , " it can also be integrated into the whole machine - manufacturing process . "

To make the film , the researchers first create a mold using lilliputian " nanospheres " that they applied to a glass surface and that self - meet into a tightly pile layer . The researchers then used the cast like a template to agitate the pattern into the picture . [ Biomimicry : 7 Clever Technologies Inspired by Nature ]
Scaling up the assembly to industrial levels would be simple to do , Wu say . They would enforce the cast to a bike and use it for roll - to - roll manufacturing , he say . Like an honest-to-goodness - school day printing pressure .
The next step for the researchers , they say , is to better the film ’s strength , finding the right balance between flexibility and hardness .
Wu said his team of researchers is very excited about the outcome they achieved . The technology can be applied to smartphones , tablets and television that are already on the market , Wu say . But it does n’t have to halt there . Because the coating is so tenuous and elastic , it could be used in the future on pliable or even foldable display .
" That even makes us more mad , " he said .
Original article onLive skill .